
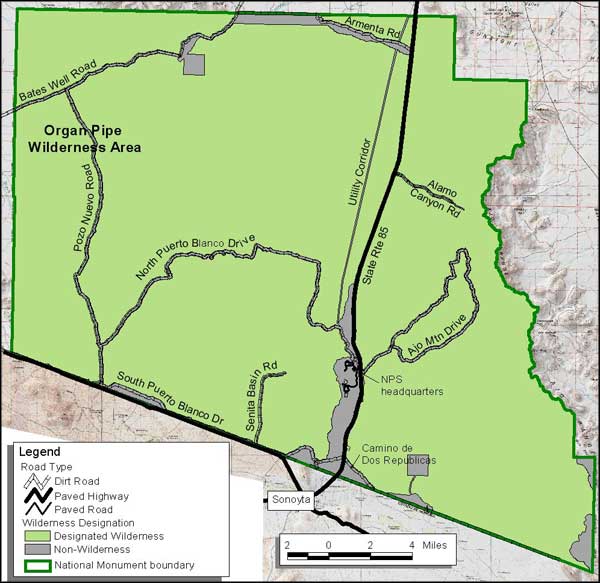
Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument Wilderness


About 312,600 acres (some 95%) of Organ Pipe National Monument are designated wilderness, and is "backcountry" by definition (and therefore presently closed to all legal access). The western boundary of Organ Pipe is against the Cabeza Prieta National Wilderness, the southern boundary against the border with Mexico.
The Ajo Range is on the eastern boundary of the Wilderness, with Mount Ajo (4,024') at its top. From there the land drops away west to a broad desert plain cut with isolated canyons and dry arroyos. The alluvial soils here support more than 550 species of plants, including the famous organ pipe cactus, a large, multi-spined species of cactus that is common in Mexico but rare in the US. As the primary pollinators in the organ pipe's breeding cycle are night-flying bats, the cactus blooms only at night in May, June and July. And each lavender-white flower lasts only one night.
Hikers and backpackers need to check with the visitor center before heading into the bush here. You never know, there may be some areas where they figure it's safe to wander in the Wilderness for awhile: the biggest problem here is that Mexican border. Second biggest problem is the near-complete lack of water. The only reliable water for many miles is at the campground near the visitor center.

Organ Pipe Cactus Wilderness Area map
