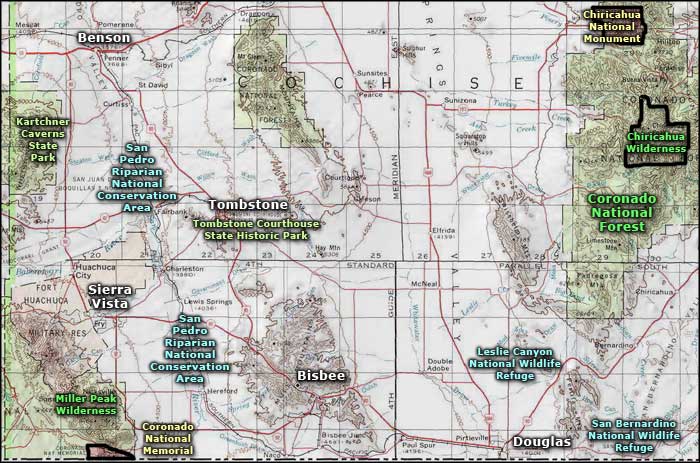
San Bernardino National Wildlife Refuge

The 2,309-acre San Bernardino Ranch was acquired by the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service in 1982 specifically to preserve the habitat of endangered native fish species and protect the water resources that feed those habitats. The property is right against the US-Mexican border and contains some of the headwaters of the Yaqui River.
The property is mostly in a north-south canyon with flat-to-rolling uplands that drop suddenly into the flat bottomlands that bisect the refuge. The uplands are dominated by Chihuahuan desert grassland and desert scrub while the bottomlands are covered with fallow fields and a mesquite bosque. A series of natural seeps and man-made artesian wells have been used in this landscape to create small alcoves of riparian vegetation and woodland, riparian scrub, cattail marshlands and other aquatic habitats.

While there's lots of birds (more than 270 species), reptiles (55 species) and mammals (62 species) at San Bernardino, the property is managed primarily for the benefit of endangered fish species like the Yaqui topminnow, Yaqui catfish, Yaqui beautiful shiner and Yaqui chub.
San Bernardino NWR is open for hiking, photography, birdwatching and hunting (dove, quail, cottontail, in season). Fishing, camping and off-road vehicular traffic are not allowed.
The refuge office is located about 16 miles northwest of Douglas while the refuge itself is about 17 miles east of Douglas.
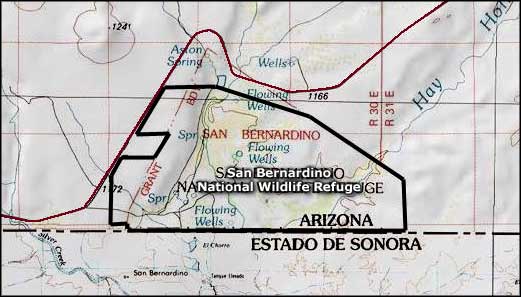
San Bernardino National Wildlife Refuge map